Home » Art
Category Archives: Art
The Pirate Captain & His Burning Prey Upon the Background Billows: An Iconic Image

Arguably only a few illustrators have matched, and none have surpassed, Howard Pyle (1853-1911) for his iconic pirate images and their contribution to the modern myth of pirates and piracy. Whether of picturesque and picaresque buccaneers, or of pirate attacks, duels, buried treasure, or extortion of prisoners, his illustrations, with few exceptions, have inspired imitation and homage.
Of all Pyle’s strikingly evocative pirate art, his painting of Captain Keitt for his novella The Ruby of Kishmoor is considered by many to be the pinnacle of his work. We see it above: the pirate captain, clearly inspired by Captain Kidd, braced seaman-fashion on the poop of his pirate ship The Good Fortune in the trough of the sea, his prey, the Rajah of Kishmoor’s great ship The Sun of the East, burning in the background upon the crest of a swell, its mainsail shot to pieces.
The ship’s lantern rises behind the pirate captain, and curiously — and surely for reasons or artistic composition — behind it the ensign staff flying the Jolly Roger. I quibble here: the lantern would historically have been astern of the flagstaff, outboard of the hull, the other inboard. Curiously, the lanterns, and in fact the stern decoration and color, of both ships appear similar if not identical (and somewhat similar ones can also be seen on Disney’s pirate ship the Black Pearl).
Keitt wears an 18th century style cocked hat (aka tricorn) with gold trim, setting off his rather ratty black hair and long mustachios framing a stern face that hints of evil, an expression suggesting he might be posing for a painter, recalling perhaps the pirate portraits in Exquemelin’s The Buccaneers of America. Or perhaps he has been caught off guard, or has been asked a stupid question.
A ratty kerchief is tied around his neck rather than a cravat, and he wears a crimson just-au-corps, waistcoat, and long swashbuckling sash. His wide loose breeches are the seaman’s, and on his feet he wears boots of some sort, perhaps intended as “sea boots” although such were worn largely by fishermen and by seamen of this era only in cold weather. The boots are a deliberate cliché or trope: even more than a century ago the audience expected to see pirates in boots, though most often of those for riding with tops folded over. Pirates wore shoes and stockings or, especially if poor, went barefooted. The idea of “pirate boots” derives via popular illustrators from those of cavaliers and musketeers.
Hanging from a buff baldric is a Spanish “bilbo” style rapier with large curved shells although he would likely have worn a cutlass instead, and from a waist-belt. A short-barreled pistol is stuffed into the sash, and Keitt holds a speaking trumpet in his hand, perhaps with which to verbally abuse those victims doubtless left behind on the burning, sinking ship — he surely no longer has any need of the trumpet for hailing. Perhaps he uses it to bellow at his crew rather than pass orders via his subordinate officers.
There is a somber aspect to the painting: those aboard The Sun of the East who did not perish in the battle and boarding action have surely been left to the severe mercy of the sea.

N. C. Wyeth’s frontispiece and dust jacket art for the US edition of Rafael Sabatini’s Captain Blood: His Odyssey (1922) is almost as famous as Pyle’s painting. Clearly an homage to his teacher’s famous painting, Wyeth’s work embraces the image of Sabatini’s eponymous hero, even if he depicts the famous literary buccaneer in more mid-17th century style rather than of the 1680s. It’s not entirely Wyeth’s fault. Foremost, he intends to evoke the novel and its hero, rather than portray them with complete historical accuracy. Further, Sabatini himself occasionally misuses terms for period dress, for example writing doublet when clearly he intends the just-au-corps, the long coat worn in the 1680s and after.
Still, Wyeth’s painting is true enough to the novel, and clearly he had read it. The illustration was first painted then later used for a novel because it was close enough, as with Wyeth’s dust jacket art and frontispiece for The Black Swan. In the painting above, Peter Blood’s hair and eyes are accurately presented — black and blue — and he has a small mustache as he did in the serialized novel but which he had lost when the novel was published.
He wears a doublet with silver-laced black sleeves, although this ought to be a black and silver just-au-corps. He wears a falling collar of Mechlin lace rather than a cravat of one, and a bullion-encrusted baldric. His hat is rather tall for the period but has the required crimson ostrich plume. The crimson feather is there to add color, but all in all Peter Blood’s dress is close enough to Sabatini’s description: “scrupulously dressed in black with silver lace, a crimson ostrich plume curled about the broad brim of his hat affording the only touch of colour.”
We can easily forgive Wyeth our quibbling criticisms, for, to repeat ourselves, the painting is intended to be figurative and evocative. It is, to quote a past editor of mine in regard to book illustrations, intended to entice potential readers to buy the book.
In the background a Spanish galleon burns, clearly an abandoned prize, although the burning of prizes, but for an English man-of-war (with a Dutch admiral, curiously) burned by the French, is not mentioned in the novel. Perhaps the image is of the Spanish fleet’s flagship Milagrosa which was to be “scuttled” after being defeated by Blood’s buccaneers. More likely, it is a generic image of one of the unnamed Spanish galleons captured by Captain Blood.
In practice burning was often easier than scuttling, particular with larger ships. Buccaneers did occasionally burn prizes, typically keeping some crew and passengers as prisoners while turning the rest loose in a boat, and occasionally sank smaller prizes as well. More often though they were likely to keep the prize or leave it with its crew and passengers, first cutting a mast down or taking some of its sails so that word of the buccaneers might not be swiftly carried to the nearest port.
Of note are the orange-gold clouds with red-black plumes of smoke in front. A sun, perhaps, setting on the galleon and Spanish Empire? Gold for plunder, and red-black for the two colors Sabatini repeatedly uses as themes in the novel?

From the 1927 et al Riverside Press Cambridge (a Houghton Mifflin imprint) edition of Captain Blood: His Odyssey, the dust jacket and front cover art by Clyde Osmer Deland (1872-1947). Although the painting is more historically accurate — no boots, correct just-au-corps and hat — it lacks the eye-catching flair of an illustration by Pyle or Wyeth, even if a burning sinking ship draws the eye. And again there’s that damned mustache that’s not in the novel! Here, Deland has no excuse, given that he painted the illustrations several years after the novel’s publication.
The ship is not burning in the illustration above, but the magazine cover was clearly inspired by Pyle and Wyeth’s paintings. The pirate depiction, in particular its resemblance to the much later Captain Jack Sparrow, is discussed here.

Another Wyeth painting hinting at an homage to his teacher Howard Pyle and which has influenced our idea of the pirate captain and his burning prey on the billows. The blue-green tropical sea is up, giving us the mountain-like billows we like to see — and which also aid in composition. The burning ship is clearly a Spanish galleon, of a style much-used by Wyeth and discussed here. That it has just been plundered is obvious: booty is piled on the poop, including a classic Pyle-style treasure chest with curved top. The buccaneer captain is almost identical to one Wyeth painted for the September 22, 1921 issue of Wall Street Number magazine, a Life magazine publication, discussed here.
The galleon rests on a crest, with the buccaneer ship below in the trough, suggesting the rover is sailing away. Classic Wyeth clouds frame the galleon, and the skull and bones — an anachronism — flies at the stern but we can see only the lower part of the field, as in Pyle’s painting at the top of the page, clearly an homage.

Yet another homage, this time Peter Hurd (1904-1984) to his teacher N. C. Wyeth. Although Hurd was best-known for his paintings and illustrations of life in the Southwest US, he edited and illustrated Marauders of the Sea, a collection of excerpts from pirate stories, 1935, with an introduction by N. C. Wyeth. In the painting, two ships are closely engaged, one of them afire. Here, the pirate captain is not standing the deck of his ship. Rather, the composition is clearly arranged after late 17th century paintings and illustrations of pirate and men-of-war captains and admirals, as will be discussed in more detail shortly.
Hurd’s pirate captain reminds us of the famous depictions of Exquemelin’s buccaneers shown farther below. His eyes are blue and his hair black, like Peter Blood’s, but he also has a Spanish-style mustache and a scar across his cheek. He wields a classic shell-hilt cutlass with large brass rather than iron shells, though all the large shells I’ve seen on cutlasses were iron — only smaller shells might be made of brass. His face is scarred, his jacket is either Spanish or an earlier English doublet, and he wears breast and backplate which Peter Blood did fictitiously and some captains of men-of-war did in reality. Whether any buccaneer captains actually did is entirely speculative, for there is no record of them doing so.
Other Notable Homages
I’ve chosen one authorized imitation of Wyeth’s “Captain Blood,” one authorized inspiration of the Pyle/Wyeth paintings, and also several notable homages, five of them to Howard Pyle’s “famous painting at the top” Captain Keitt,” and rest to Pyle and perhaps to Wyeth and others as well — an homage to homages and to the original.



Three illustrations by George Alfred Williams, the first from The Boy’s Book of Pirates and the Sea Rovers by George Alfred Williams (New York: Frederick A. Stokes Company, 1913). It is a likely homage to Pyle’s painting — and only five years afterward. The second and third are from The Pirates of Panama or The Buccaneers of America by John Esquemeling (New York: Frederick A. Stokes, 1914). Both are clearly homages to Pyle’s famous painting. All three doubtless contributed to the image of the iconic image of the pirate captain and his burning ship on the background billows.




The first image of the four just above is the front cover of the program for the 1924 film version of Captain Blood (Vitagraph) at Astor Theatre, Broadway and 45th, in New York City. The image was also used on a poster for the film. The cover style has been copied from a combination of the dust jacket of the 1922 US release of the novel and of the front board of the book. I’m no fan: here Captain Blood looks more like an unadventurous bourgeois dressed as a pirate for a costume party, rather than the long, lean, hawk-faced adventurer-physician-buccaneer described in the novel.
The likeness is intended to represent J. Warren Kerrigan who played the starring role. Perhaps the unknown illustrator was getting a dig in at Kerrigan and felt the same way I do about him. The actor famously told The Denver Times during the First World War that “I am not going to war. I will go, of course, if my country needs me, but I think that first they should take the great mass of men who aren’t good for anything else, or are only good for the lower grades of work.” Clearly he was no Sabatini-esque hero in real life, nor even an Errol Flynn, at least in regard to courage, panache, dignity, and empathy.
The bottom image is a copy of one of the many posters designed for the 1924 film, clearly inspired by both Pyle and Wyeth. Atypically, the ship is exploding rather than simply burning, although the latter often led to the former.
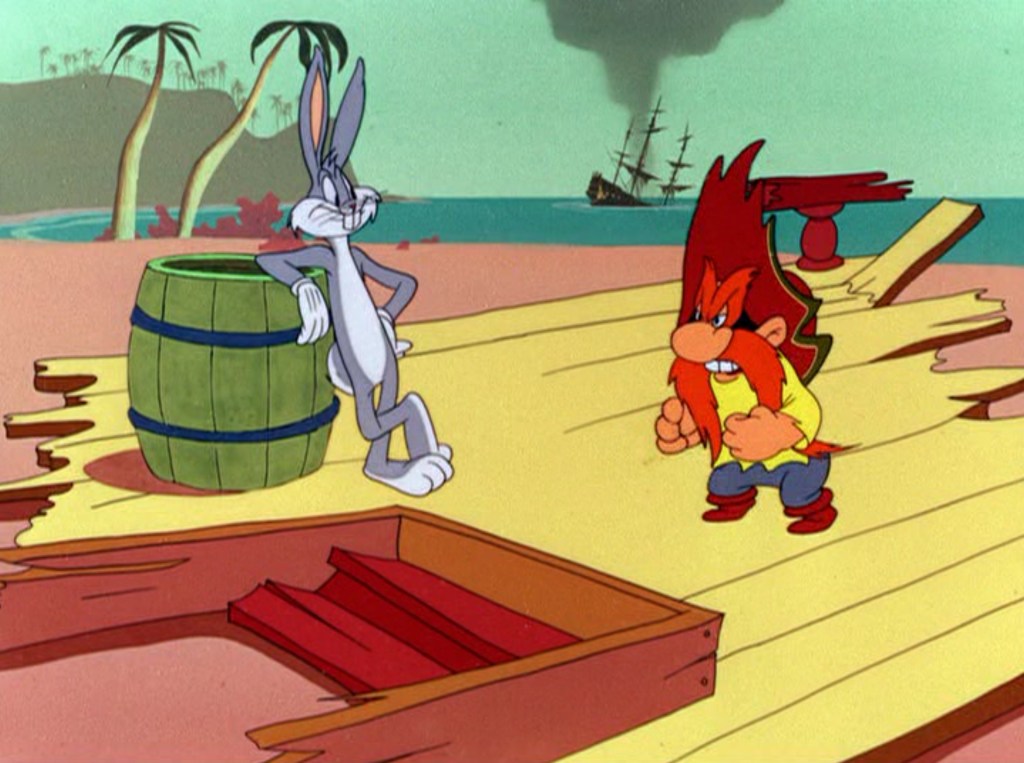
The writers and artists of “Buccaneer Bunny” (Warner Bros. Looney Tunes, 1948) clearly intended an homage to Pyle and Wyeth. It’s basically a reverse or mirror image of the Captain Blood cover art and frontispiece done by N. C. Wyeth. DVD screen capture.
Above is a possible homage to Pyle and Wyeth: Errol Flynn as Brian Hawke just having rescued Alice Kelley as Princess Padma from the burning ship of the Mughal Emperor. Compare with The Goonies screen capture below.
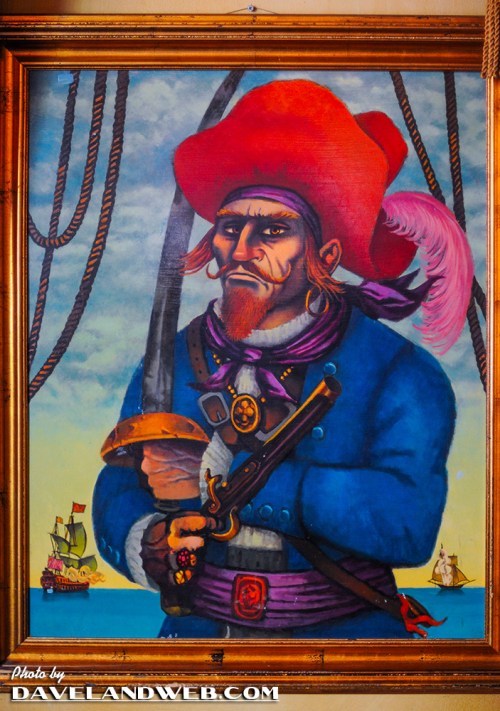

In the painting above there is no burning ship, but one firing a broadside instead. Even so, the image is clearly inspired by the paintings of Pyle and Wyeth, and as much by the illustrations from Alexandre Exquemelin’s The Buccaneers of America discussed below. The painting, artist unknown but suggested by some to be Ed Kohn, has hung for many years in the Pieces of Eight store adjacent to the Pirates of the Caribbean ride at Disneyland. Originally it hung in the Pirates Arcade Museum (mostly an arcade) before the shop replaced it in 1980. It may depict Fortune Red, the animatronic fortune teller in the arcade.
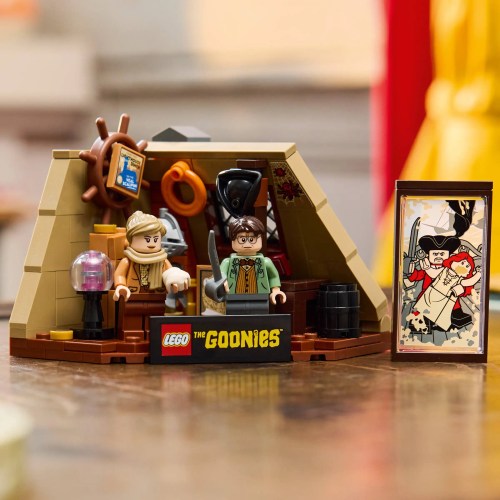
Above, an homage if you like, and clearly a comic riff, on Pyle’s famous painting. A damsel-in-distress has been added — and Chunk’s tongue too… From the attic scene in The Goonies, 1985. Compare with the Against All Flags screen capture above it.
The Goonies painting as imagined by Lego, part of a kit (“The Goonies: The Walshes’ Attic”) to accompany The Goonies ship and the film scenes depicted inside.

I hesitated to post the image above, of Arnold Schwarzenegger as Captain Blood by William Stout. The film was under consideration in 1994, and, although I have great respect for the former Governor of California as an action hero, I am overjoyed that the film never made it into production. The proposed script was of a sort commonly pitched by studio executives, producers, and screenwriters: one intended solely to make money (art, artist, and audience be damned).
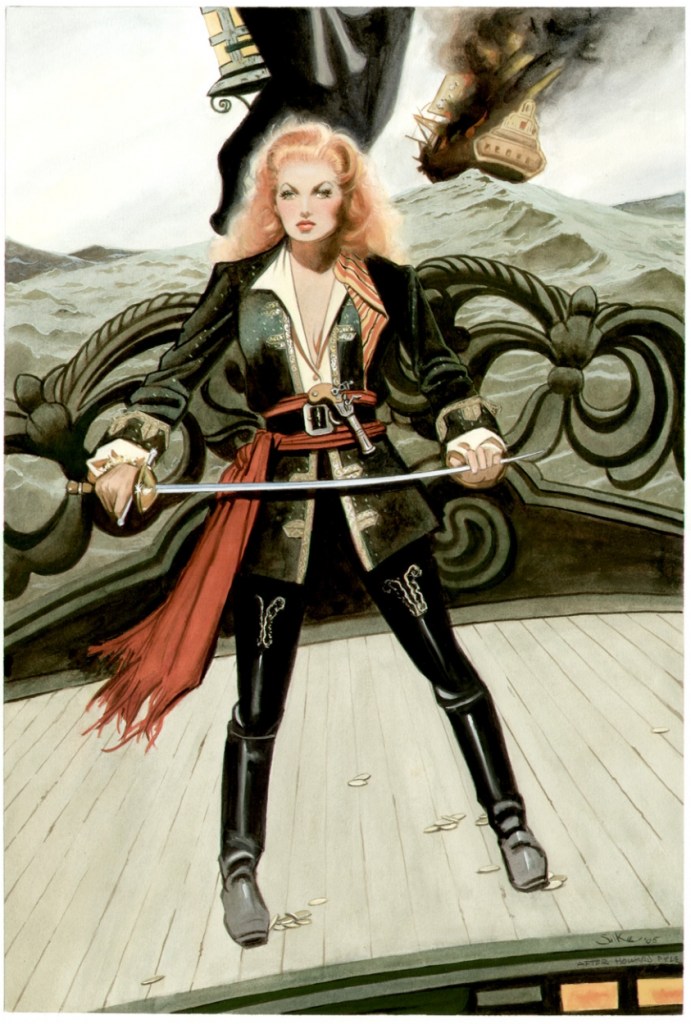
Above is an homage by arts and entertainment polymath Jim (James R.) Silke (1931-present) to Howard Pyle’s famous painting (see “After Howard Pyle” below the signature on the painting above) featuring Maureen O’Hara as Spitfire Stevens in Against All Flags (1952), also starring Errol Flynn. The 2005 work was created as a commission for Brian Peck.
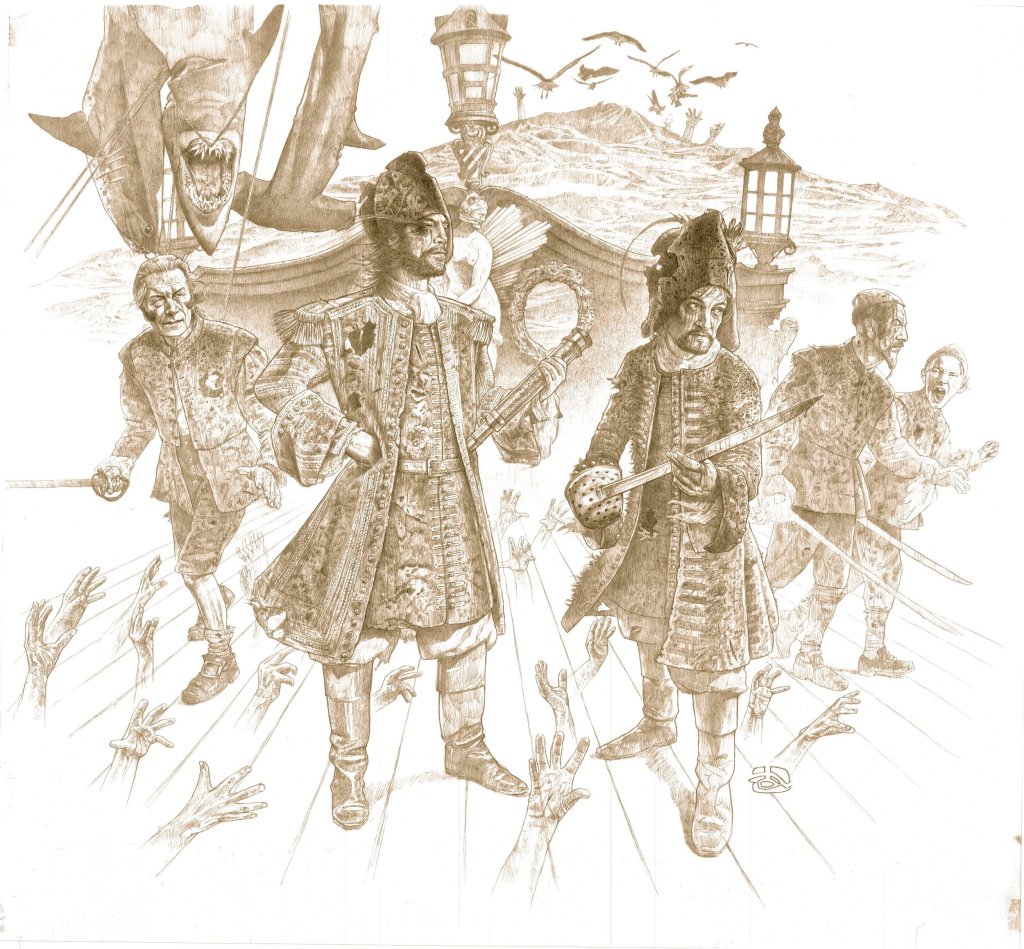

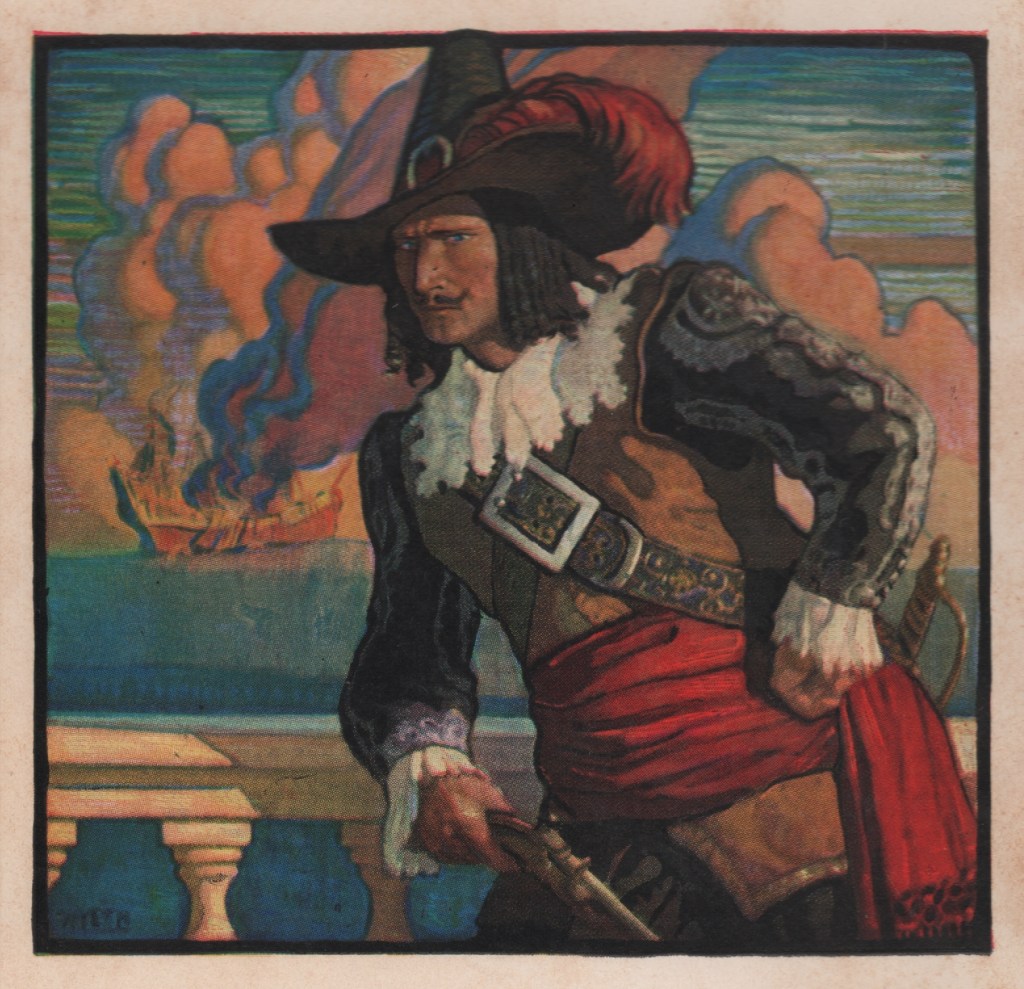
My good friend Antón Viejo Alonso brought the image above to my attention. Drawn by noted portrait artist and film costume concept illustrator Darrell Warner for Pirates of the Caribbean: Dead Men Tell No Tales (Disney Studios, 2017), it is clearly an homage to the Howard Pyle painting at the top of the page.
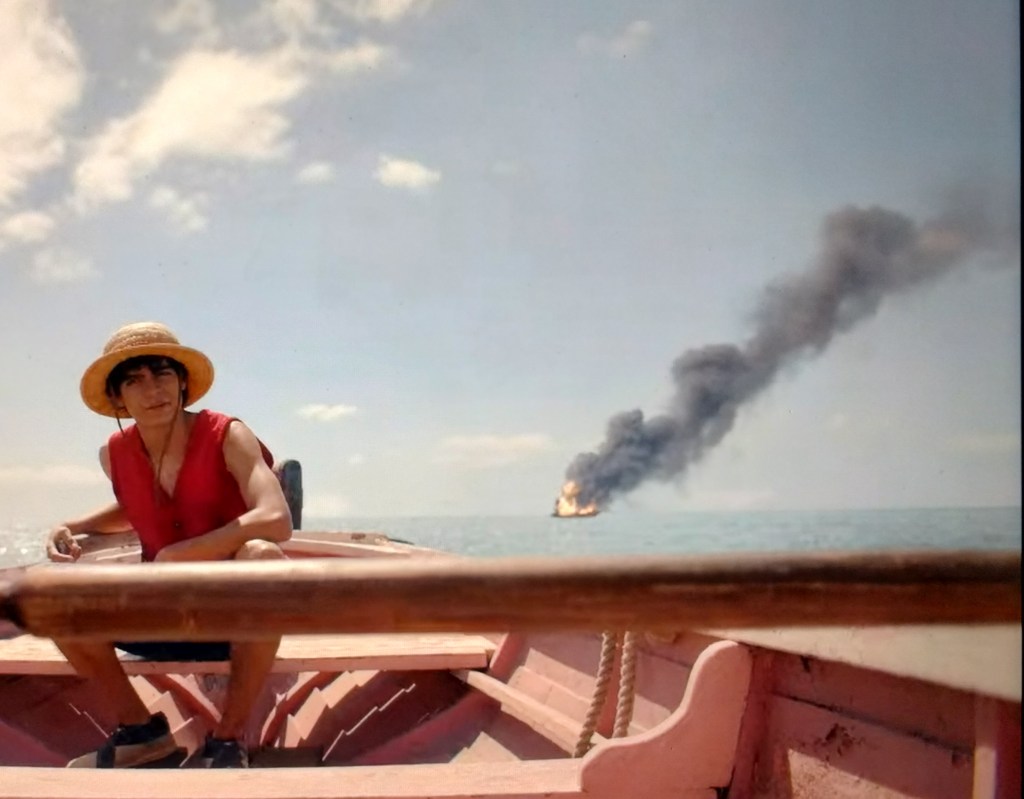

A cropped image from Netflix’s live action 2023 release of One Piece, with pirate-captain-to-be Monkey D. Luffy (played by Iñaki Godoy) in the foreground (foresea? :-)) with a burning ship in the “backsea,” clearly an homage to Pyle, Wyeth, et al. Furthering this argument is the fact that the scene with burning ship is not in the original manga written and illustrated by Eiichiro Oda nor in the anime based on it produced by Toei Animation. (N. B. there is a similar scene when the [Spoiler Alert!] Going Merry burns and sinks much farther along in the voyages of the Straw Hat Pirates, which is perhaps an homage [Spoiler Alert!] to Peter’s Blood’s loss of his beloved Arabella).
Inspirations & Influences
The most likely inspiration — the seed planted in the subconscious — might well be some of the original illustrations in Alexandre Exquemelin’s early Dutch, Spanish, and English editions of The Buccaneers of America. They include several portraits of famous buccaneers, although we have no idea how accurate the depictions are, but this matters little in regard to inspiration.



The three illustrations above are Spanish edition copies of the originals in the Dutch 1678 edition: Francois L’Ollonois, Bartholomew Portuguese, and Henry Morgan. All show battles, including sea fights, raging in the background, with billowing smoke suggesting that some ships may be afire. None of these buccaneer captains — as far as we know — are standing on the the decks of the ships. It took Howard Pyle’s genius to compose a portrait evoking the adventure and romance, at least as we believe it to have been, of piracy on the high seas.
The illustrations in Exquemelin’s books were doubtless inspired by a common form of portraiture associated with fighting seamen and soldiers, officers in particular for typically only they could afford portraits or had enough social status that a patron might commission a portrait of them.


The two portraits above are typical of those of the era: the subject in the foreground, with a depiction of a major associated action in the background. Myngs, prior to becoming an admiral, led a number of raids on the Spanish Main, with buccaneers-as-privateers as his consorts, after the English captured Jamaica from Spain. The portrait of Montague shows us a burning ship, but it may not be that of an enemy. It appears to be of English build, and is therefore more likely the HMS Royal James, Montague’s flagship burned by a Dutch fireship in 1672, resulting in Montague’s death.
Not quite yet a buccaneer or pirate in the photograph above, nor yet a burning ship on the background billows — but aspirations enough. 🙂
Copyright Benerson Little 2024. First posted 24 September 2024. Last updated November 1, 2025.
“The Buccaneer Was a Picturesque Fellow” by Howard Pyle

And indeed he was a picturesque — and picaresque! — fellow, the buccaneer! Howard Pyle’s painting of this romantic sea rover has influenced the imaginations of half a dozen generations of readers, writers, illustrators, costume designers, film-makers, and game designers. Currently on view at the Delaware Art Museum, the painting was one of four created for an article, “The Fate of a Treasure Town,” also by Pyle, published in Harper’s Monthly Magazine, December 1905.
In fact, the paintings accompanying the article are some of Pyle’s most famous buccaneer and pirate images. In addition to the picturesque buccaneer, there is “An Attack on a Galleon,” “Extorting Tribute from the Citizens” (used as the cover of The Buccaneer’s Realm, for what it’s worth), and “So the Treasure Was Divided.” Of the most famous paintings of his buccaneer, as opposed to pirate, series, only “Which Shall be Captain?” for “The Buccaneers” by Don C. Seitz, in Harper’s Monthly Magazine, January 1911, and “How the Buccaneers Kept Christmas,” Harper’s Weekly, December 16, 1899, are missing. (High resolution images are available on Wikimedia Commons.)

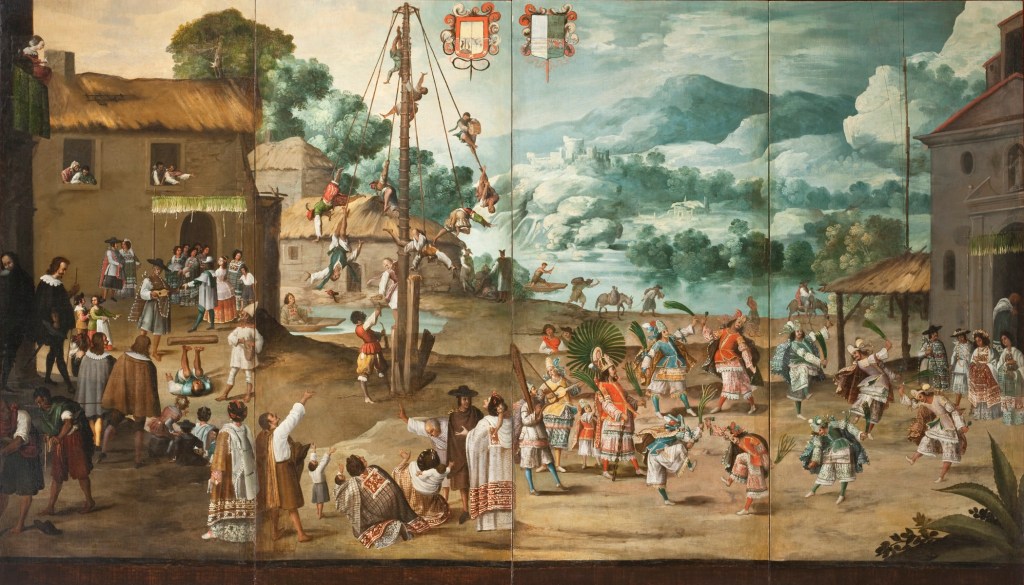
Pyle’s article opens with romantic tropical buccaneering scene-setting, then shifts in detail to the sack of Cartagena de Indias in 1697, a privately-funded French privateering expedition that was composed of hired ships and troops of the French navy and army, with a large body of French buccaneers and Caribbean militia in support. The Baron de Pointis, commander of the expedition, swindled the buccaneers out of their agreed share, so they returned and extored more treasure from the citizenry. Pyle’s painting, “Extorting Tribute from the Citizens,” shows buccaneers actively engaged in this pursuit. (On a side note, the painting was used for the dust jacket of The Buccaneer’s Realm, my second book.)
But few people have actually the read the article or even know about the sack of Cartagena de Indias, and it’s the images themselves that have caught our imagination. In particular, film-makers, illustrators, and Disney have borrowed heavily from the paintings: from The Black Pirate of Douglas Fairbanks and the Captain Blood of Michael Curtiz, to Disney’s Pirates of the Caribbean attraction and films, to the sea rover art of Don Maitz, Pyle’s influence is impossible to deny.

From a historical standpoint, the paintings are far more evocative than accurate, although clearly Pyle attempted to get historical details correct. But this wasn’t easy. He had to interpret written descriptions and also — the bane of truth-seeking historians and researchers everywhere! — appeal to popular tropes as well. For popular works, some degree to catering to popular expectations is considered mandatory, or so I’ve been advised (and immediately resisted, bound by nature to do my best to keep within the limits of fact and fact-finding, at least as much as possible).
For Pyle, it was not the buccaneer or pirate’s sea roving escapades that made him appealing: “It is not because of his life adventures and daring that I admire this one of my favorite heroes; nor is it because of blowing winds nor blue ocean nor palmy islands which he knew so well; nor is it because of gold he spent nor treasure he hid. He was a man who knew his own mind and what he wanted.”
He conveyed this well with his picaresque — sorry, picturesque — buccaneer even if it appears that the young man evokes a purely romantic image of a sea roving adventurer rather than a real one.

Let’s take a quick look at his arms, accoutrements, and clothing and compare them to the historical. We’ll begin with his hat. Spotting the red ball tassels, we assume the hat is intended to evoke Spain — it’s the somewhat tropish hat of a Spanish flamenco dancer or mounted matador. Perhaps the buccaneer captured it, or, I think more likely, the buccaneer is in fact a Spaniard, a mestizo perhaps. We know that there were Spanish renegados among the buccaneers. Let’s keep this in mind as we look at the rest of him.
He’s wearing two gold earrings — small simple hoops. Most European-derived buccaneers did not wear earrings, with the occasional exceptions of the Dutch (single pearl, single ear) and fops (single pearl, single ear). However, all too often our impression of pirates is influenced by our ethnocentrism: some Africans, Native Americans, mulattos, and mestizos in the Americas did in fact wear earrings. Pyle probably added earrings as part of the expected pirate cliché, but to my mind, the earrings, considered historically, are more evidence that this buccaneer is a Spanish mestizo renegade, as is the perhaps fanciful bracelet on his wrist. His dark hair and olive skin — also “Spanish” clichés — are to me more evidence of his Hispano-American origin.
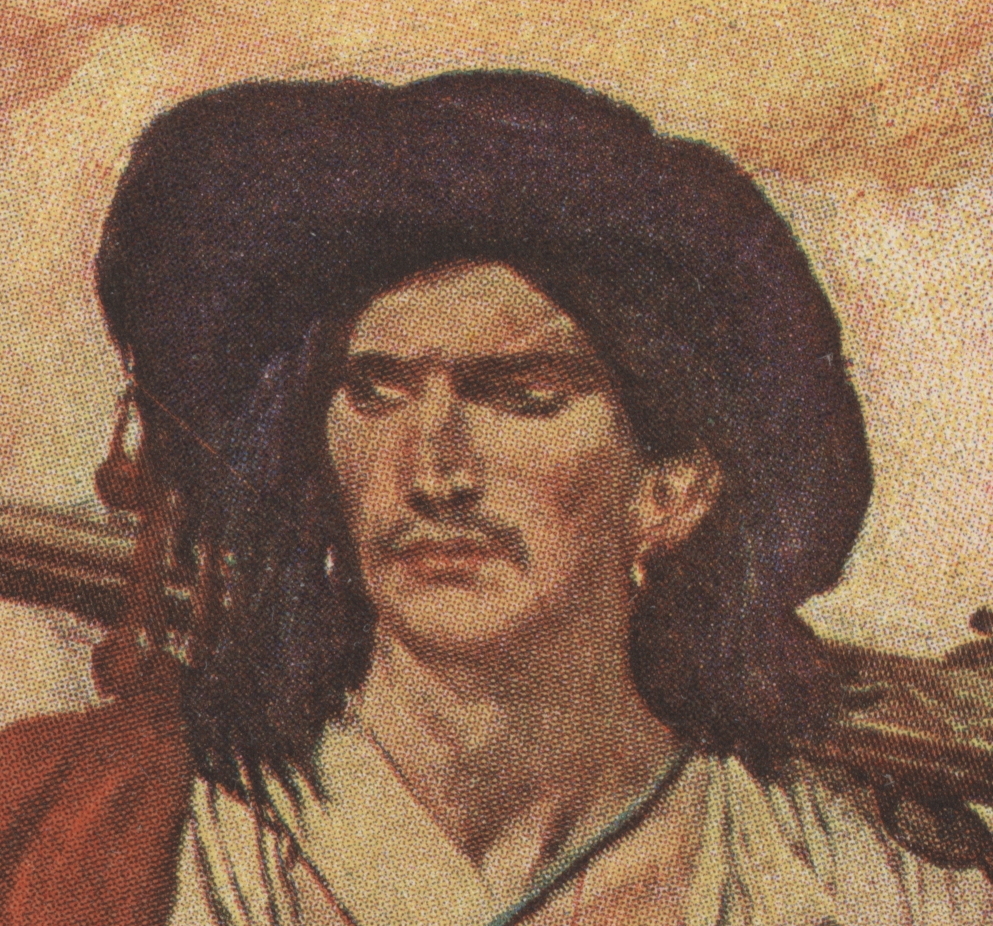

He has a red cloak over his shoulders, but would a buccaneer wear one? Probably not in the daytime, given the highs in the upper 80s and lows in the upper 70s year-round in Cartagena de Indias, although in some areas of the Caribbean cloaks, jackets, blankets, “ruggs,” &c were worn or used, typically at night. That said, a 1680s image, if not eyewitness then at least based on eyewitness descriptions does show a Spanish pirate or privateer with a cloak! More on this below.
Further, French priest and eyewitness Jean-Baptiste Labat described the admiral of the Armada de Barlovento in the Caribbean as wearing a cloak, but he was an old man and perhaps needed the cloak to keep his old bones warm at sea. And Spaniards wearing them are depicted in period images of New Spain, see the last image below for example. Perhaps, as with the Spaniard’s ruff which was often added historically as a satirical symbol — Spaniards no longer wore ruffs –, Pyle added the buccaneer’s cloak as a mere symbol of dress to indicate that the man is a Spaniard. This isn’t the first time Pyle put a cloak on a buccaneer: he also did so in his painting, “How the Buccaneers Kept Christmas,” Harper’s Weekly, December 16, 1899.
His “musket” is a bit of an anachronism: it is a Jaeger or Jaeger-type hunting rifle. Developed in the late 17th century in the region later to become known as Germany, there is no indication they were ever used by buccaneers. These Caribbean sea rovers used the long fusil boucanier, especially among the French, and various other muskets at times. However, there are instances of carbines (Sp. carabinas) in use on occasion at sea and ashore, and we will assume this is what Pyle meant to represent. His pistol could represent any number of sea pistols in use at the time, and is close to their common size. Its lock is indeterminate, but it hints of a Spanish Miquelet style.

His rapier, or possibly broadsword, is a shell-hilt, of what could be a Spanish-style doble concha, although the true cup-hilt (taza) was far more common. All or nearly all English, French, and Dutch buccaneers carried cutlasses, although there are documented indications of a few exceptions for smallswords and broadswords. However, the rapier — espada ropera — was still in common use in Spain, Portugal, and Spanish-governed parts of Italy at the time, not only among gentlemen (and most Spaniards considered themselves gentlemen!), but also among soldiers and almost surely among some seamen and artilleros. In fact, the eyewitness, or nearly so, image below of a Spanish privateer or pirate from the 1680s shows him wearing a Spanish rapier. Curved quillons were uncommon on Spanish swords of the era, although they did begin to show up on some at the end of the 17th century. Again, although for Pyle the rapier may have been a necessary trope, historically it would point the buccaneer being a Spaniard, Portuguese, Italian, or Corsican.
His sash is a bit wide, at least from what eyewitness images suggest, but his belt is correctly worn over it. The pouch or box on his right may be a cartouche box worn on a strap in a rather un-buccaneer style. His breeches, buttoned at the sides, are quite typical of those shown worn by Spaniards in the era, although Pyle may have depicted this style to evoke the swashbuckler or pirate as he did in other paintings, “I Had Met My Equal” for example.
And last, his sandals: most buccaneers, according to eyewitness descriptions and images, wore conventional shoes, or boucanier shoes made from skin pulled from the hocks of hogs (see here for details), or went barefoot, at least among the poorest sort. However, as noted not all buccaneers were English, French, or Dutch. Some were Spanish renegades, including Spanish Native Americans and mestizos, and we know that some of both groups wore sandals at the time.
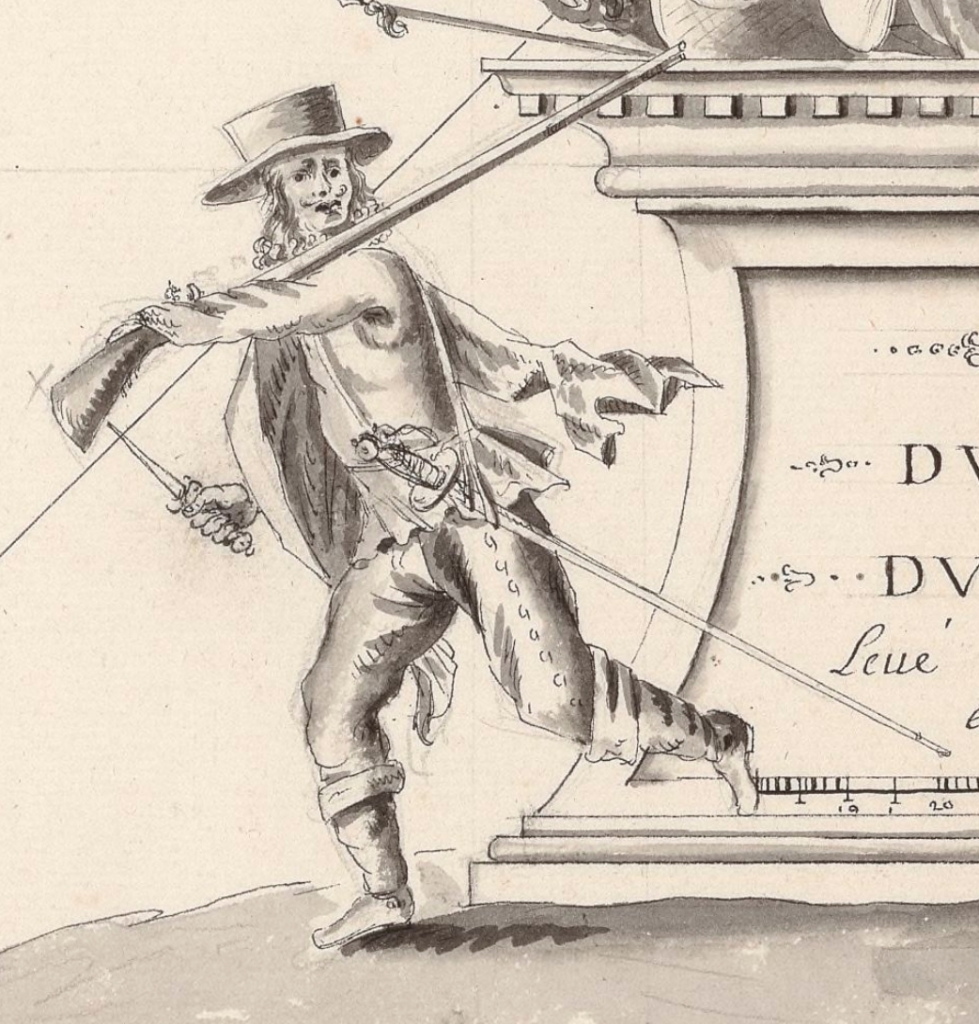
The image below was drawn by a French engineer in the 1680s, almost certainly based on local eyewitness accounts of French pirates or privateers who attacked Nipe on Saint-Domingue (modern Haiti). There is no chance Pyle ever saw this image, yet his picturesque buccaneer evokes it well! The Spaniard is even wearing a cloak! Many Spanish pirates and privateers — most, some eyewitnesses noted — were men of color: Native Americans, mestizos, Africans, and mulattos. Is this what Pyle intended, a Spanish or mestizo renegade buccaneer? I can’t be entirely certain, but the evidence and my gut assure it is.
Bookends, Bookcovers, & More…
The painting has inspired a variety of objects and art, ranging from bookends to bookcovers to game miniatures. The bronze-clad bookend below, “Pirate’s Den” by Peter Manfredi (1930) for the Pompeian Bronze Co., is a three dimensional copy of Pyle’s painting. This example is one of two variants; the other has part of the background removed.

The Pompeian statuette bookend below, “Buccaneer” by Peter Manfredi (1930), was clearly inspired by Pyle’s painting. On the left is “Miss Pirate” by the same sculptor and year for Pompeian Bronze Co., Brooklyn.

In The Black Swan (20th Century-Fox, 1942), only loosely based on Rafael Sabatini’s novel of the same name, Tyrone Power’s costume is clearly based on, and probably an homage to, Pyle’s famous painting. The hat with tassels hanging from it, the cape, the sash, the rapier, are all clearly intended to evoke Pyle’s picturesque buccaneer.

The image was clearly the inspiration for this detail on the 1952 “one sheet” (full size 27″ by 41″) poster for Against All Flags starring Errol Flynn, Maureen O’Hara, and Anthony Quinn.

The image has been used often on the covers of trade paper editions of Captain Blood: His Odyssey by Rafael Sabatini. The one below is published by the Naval Institute Press. Pyle’s painting doesn’t evoke the urbane and sedulous Captain Peter Blood, but it does evoke the buccaneers he led. In fact, part of the novel takes place during the sack of Cartagena de Indias, although Sabatini moves the attack on the beautiful city up in time.
The painting inspired the cover of a mass market edition of Cup of Gold by John Steinbeck, a fictional, and quite literary, account of famed buccaneer Henry Morgan.
CrossGen published a series of six comic books 2003-2004 by Chuck Dixon, Steve Epting, and Frank D’Armata featuring a Spanish female pirate hunting captain, Donessa Cinzia Elena Marie Esperanza Diego-Luis Hidalgo (seriously!). Captured by buccaneers in 1687, she turns them into pirate hunters to seek out and destroy their pirate lord in return for the location of a great treasure. Commanding El Cazador, she is known by her English and French crew as Lady Sin and Captain Sin. She appears on the cover of Issue 5 (March 2004) in an homage to Pyle’s Picturesque Buccaneer. My many thanks to Antón Viejo Alonso for reminding me of this comic book cover!

The Naxos re-release of these film music classics by the Brandenburg Philharmonic Orchestra uses the picturesque buccaneer on the “album” cover, albeit reversed. Good music too!
Firelock Games created a special edition figure as an homage to Howard Pyle for its popular (and quite historically accurate) Blood & Plunder tabletop wargame. (Full disclosure: I’ve done quite a bit of consulting for Firelock Games.)

Even produce growers, or at least one of them, have appropriated the swashbuckling image…

Perhaps the most significant homage to Pyle’s painting came from another great illustrator: Norman Rockwell. But Rockwell’s buccaneer is no longer the youthful adventurer with a touch of arrogance, but a tired grizzled veteran with torn cloak and shirt, a sash of a different color, a hat that has long lost its tassels, and a leg lost to a broadside, yet who keeps sailing the Main with his buccaneer brethren even as he begins to long for home. There are a few anachronisms, as there always are in such paintings: his pistol is of a later era, as is the cutlass that has replaced his rapier, and his boots are entirely fanciful and unhistorical — pirates didn’t wear any such footwear. But I find no real fault with such details. As I said, these are evocative, not historical images.
But I do find fault with the home Rockwell has the buccaneer dream of, for it evokes Olde England as N. C. Wyeth might have painted it — perhaps even the Admiral Benbow Inn! — and not Spanish America. I imagine our Spanish renegade buccaneer, young and old, longing instead for a place along the Spanish Main: Campeche or Veracruz, Havana or Matanzas, Puerto Bello or Maracaibo. Or perhaps he’s even from Spain! But no matter: he has chosen to sail with the hated buccaneers, and might never see his home or family again. But let us remember that these are only paintings, only part of the story: we might fill and finish the buccaneer’s tale as we please.

Copyright Benerson Little 2022. First posted August 17, 2022. Last modified September 12, 2024.